|
DEFINITION
|
|
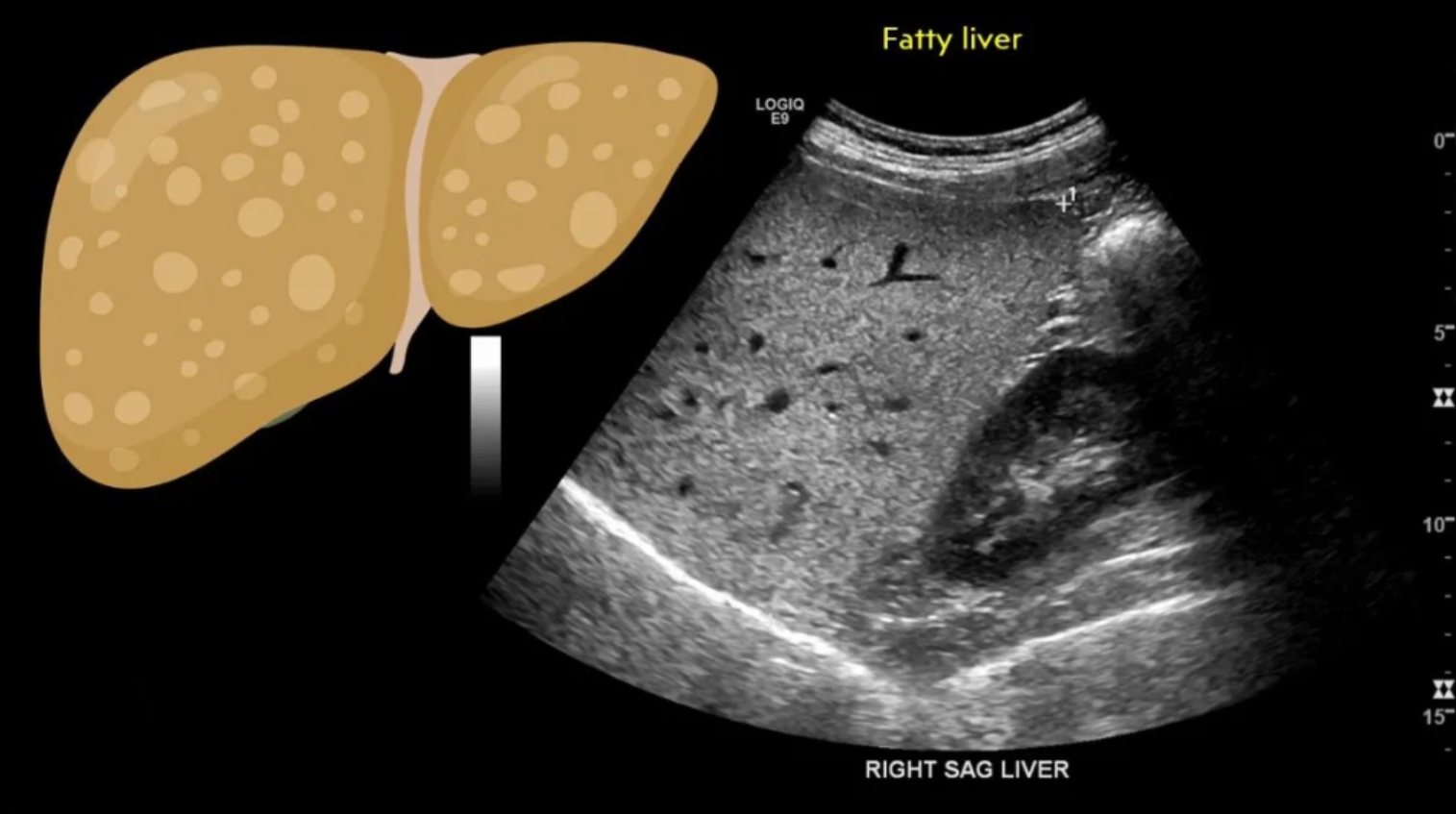
- Fatty liver disease is a common condition caused by the storage of extra fat in the liver
|
|
SYMPTOMS
|
|
- Swollen belly
- Enlarged blood vessels underneath your skin
- Larger-than-normal breasts in men
- Red palms
- Skin and eyes that appear yellowish, due to a condition called jaundice
|
|
CAUSES
|
|
- Are obese
- Are malnourished
- Have chronic viral hepatitis, especially hepatitis C
- Have genes that make you more likely to get it
- Are an African-American or Hispanic male
- Age -- the older you are, the more likely it
- You are overweight or obese
- Your body doesn’t respond to insulin as it should (called insulin resistance) or if you have type 2 diabetes
- You have high levels of triglycerides or “bad” (LDL) cholesterol, or low levels of “good” (HDL) cholesterol
- You’re older
- You have polycystic ovary syndrome
- You have sleep apnea
- You have an underactive thyroid (the doctor will call this hypothyroidism)
- You have an underactive pituitary gland (you’ll hear this called hypopituitarism)
- You’re malnourished
- You’ve lost weight rapidly
- You’ve been exposed to certain toxins and chemicals
- You have metabolic syndrome.
- Large waist size
- High triglycerides or LDL cholesterol
- Low levels of HDL (good) cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- High blood sugar
|
|
RISK FACTORS
|
|
- Have type 2 diabetes and prediabetes
- Have obesity
- Are middle aged or older (although children can also get it)
- Are Hispanic, followed by non-Hispanic whites. It is less common in African Americans.
- Have high levels of fats in the blood, such as cholesterol and triglycerides
- Have high blood pressure
- Take certain drugs, such as corticosteroids and some cancer drugs
- Have certain metabolic disorders, including metabolic syndrome
- Have rapid weight loss
- Have certain infections, such as hepatitis C
- Have been exposed to some toxins
|
|
DIAGNOSIS
|
|
- Health history
- Physical exam
- Blood tests
- Imaging tests
- Liver biopsy
|
|
MANAGEMENT
|
|
- Drink in moderation:
- Protect yourself from hepatitis C:
- Check before you mix meds or alcohol
- Eat healthy food.
- Stay at a healthy weight
- Exercise
|
|
COMPLICATIONS
|
|
- Fluid build-up in your abdomen
- Swollen veins in your oesophagus that can burst and bleed
- Confusion and drowsiness
- Liver cancer
- Liver failure
|